Current issue
Online first
Archive
About the Journal
Aims and scope
Publisher and Editorial
Advertising policy
For Authors
Paper review procedures
Procedures protecting authentic authorship of papers
Paper preparation manual
Plagiarism check
Publication ethics
Reviewers
APC
Editorial and Scientific Board
Contact
Reviewers
Analysis of methods for estimating pollutant emissions from marine engines in terms of their use for evaluating ambient air quality
1
Environment Protection Centre, Motor Transport Institute, Poland
2
Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Polish Naval Academy, Poland
Submission date: 2025-02-13
Final revision date: 2025-05-07
Acceptance date: 2025-05-10
Online publication date: 2025-06-06
Publication date: 2025-08-28
Corresponding author
Magdalena Zimakowska-Laskowska
Environment Protection Centre, Motor Transport Institute, Jagiellońska 80, 03-301, Warszawa, Poland
Environment Protection Centre, Motor Transport Institute, Jagiellońska 80, 03-301, Warszawa, Poland
Combustion Engines 2025,202(3), 3-10
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
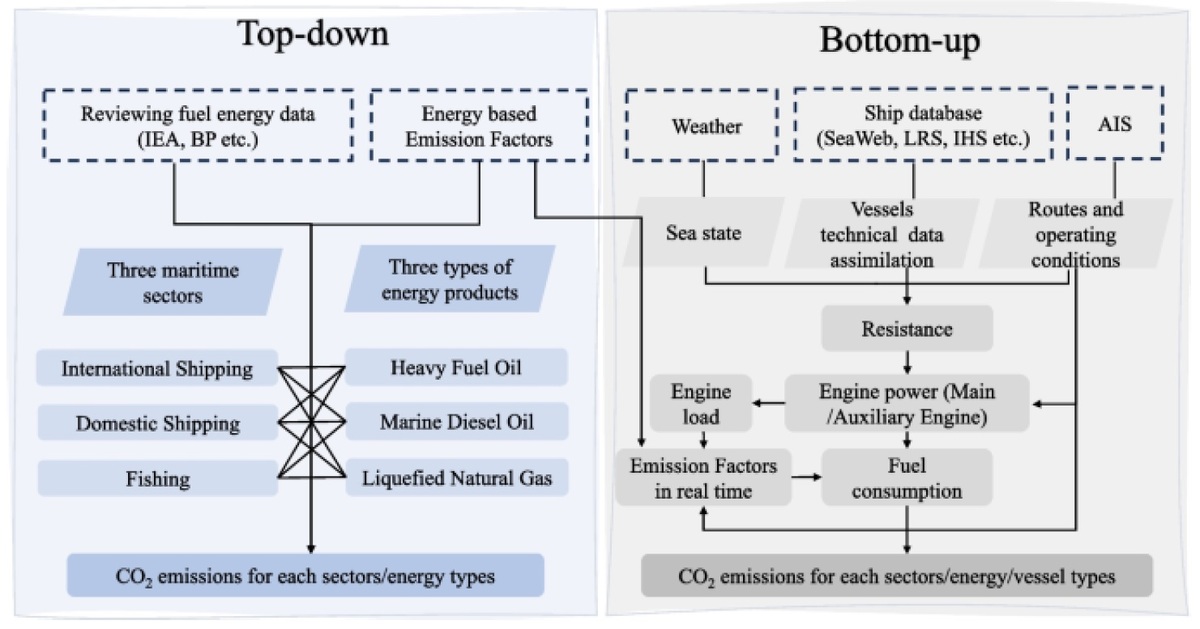
This paper discusses a method for estimating pollutant emissions from ICE of ships for air quality modelling. Three levels of emission estimation and methods for estimating ship pollutant emissions are divided into bottom-up and top-down approaches. The bottom-up approach is based on detailed ship operations and requires knowledge of many input parameters (a more accurate method but is very time-consuming). The top-down approach is based on the value of the fuel consumed by the ship and is less precise but more accessible to apply. Various data sources are available for estimating pollutant emissions from ships, including studies commissioned by the IMO, which provide reliable emission estimates for different types of ships but lack geospatial information; the CEDS database, which optimises regional emissions information by scaling emissions from ships to national levels; CAMS-GLOB-SHIP, which provides emissions at a resolution of 0,25° × 0,25° for the following substances: CO, NOx, VOC, EC, OC, BC, SOx, SO4; the EDGAR database, which provides annual emissions estimates at a resolution of 0.1° × 0.1°, but only covers the three main GHGs and F-gases; the Automatic Identification System (AIS), which provides high-resolution ship traffic data, allowing for a more realistic description of emitters. Many methods are available for estimating ship emissions, each with advantages and disadvantages. The choice of method depends on the available data and the level of accuracy required. The availability of AIS data allows for more accurate emission estimates, which is significant for a better understanding of the impact of shipping on air quality.
REFERENCES (49)
1.
Beirle S, Platt U, von Glasow R, Wenig M, Wagner T. Estimate of nitrogen oxide emissions from shipping by satellite remote sensing. Geophys Res Lett. 2004;31(18). https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL....
2.
Bogdanowicz A, Kniaziewicz T, Zadrąg R. The emission of harmful compounds from the marine diesel engine fueled by a blend of n-butanol and marine fuel. Combustion Engines. 2021;187(4):90-95. https://doi.org/10.19206/CE-14....
3.
Bojić F, Gudelj A, Bošnjak R. An analytical model for estimating ship-related emissions in port areas. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023;11(12):2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11....
4.
Browning L, Bailey K. Current methodologies and best practices for preparing port emission inventories. ICF Consulting Report to Environmental Protection Agency. 2006.
5.
Corbett JJ, Winebrake JJ, Green EH, Kasibhatla P, Eyring V, Lauer A. Mortality from ship emissions: a global assessment. Environ Sci Technol. 2007;41:8512-8518. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0716....
6.
Deng S, Mi Z. A review on carbon emissions of global shipping. Mar Dev. 2023;1(4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44312....
7.
Deniz C, Kilic A. Estimation and assessment of shipping emissions in the region of Ambarlı Port, Turkey. Environ Prog Sustain. 2010;29:107-115. http://doi.org/10.1002/ep.1037....
8.
European Environment Agency, EMEP/EEA air pollutant emission inventory guidebook 2013 – technical guidance to prepare national emission inventories, Publications Office. 2013. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.....
9.
Etienne L, Devogele T, Bouju A. Spatio-temporal trajectory analysis of mobile objects following the same itinerary. Int Arch Photogramm. 2010;38:86-91.
10.
Goldsworthy L. Exhaust emissions from ship engines – significance, regulations, control technologies. Australian and New Zealand Maritime Law Journal. 2010;24:21-30.
11.
Goldsworthy L, Goldsworthy B. Modelling of ship engine exhaust emissions in ports and extensive coastal waters based on terrestrial AIS data- an Australian case study. Environ Modell Softw. 2015;63:45-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envs....
12.
Howitt OJA, Revol VGN, Smith IJ, Rodger CJ. Carbon emissions from international cruise ship passengers' travel to and from New Zealand. Energ Policy. 2010;63:45-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpo....
13.
Huang L, Wen Y, Geng X, Zhou C, Xiao C, Zhang F. Estimation and spatio-temporal analysis of ship exhaust emission in a port area. Ocean Eng. 2017;140:401-411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocea....
14.
IMO. Third IMO Greenhouse Gas Study 2014. International Maritime Organization: London 2014.
15.
INFRAS AG: HBEFA Handbook emission factors for road transport 4.2, INFRAS, Bern 2022.
16.
Jalkanen, JP, Brink A, Kalli J, Pettersson H, Kukkonen J, Stipa T. A modelling system for the exhaust emissions of marine traffic and its application in the Baltic Sea area. Atmos Chem Phys. 2009;9;23. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-....
17.
Jalkanen JP, Johansson L, Kukkonen J. Comprehensive inventory of the ship traffic exhaust emissions in the Baltic Sea from 2006 to 2009. Ambio. 2014;43:311-324. http://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-....
18.
Jalkanen JP, Brink A, Kalli J, Pettersson H, Kukkonen J, Stipa T. A modelling system for the exhaust emissions of marine traffic and its application in the Baltic Sea area. Atmos Chem Phys. 2009;9:9209-9223. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-....
19.
Jalkanen, JP, Johansson L, Kukkonen J. A comprehensive inventory of ship traffic exhaust emissions in the European Sea areas in 2011. Atmos Chem Phys. 2016;16:71-84. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16....
20.
Johansson L. Emission estimation of marine traffic using vessel characteristics and AIS-data. Aalto University 2011.
21.
Johansson L, Jalkanen JP, Kukkonen J. Global assessment of shipping emissions in 2015 on a high spatial and temporal resolution. Atmos Environ. 2017;167:403-415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmo....
22.
Kao SL, Chung WH, Chen CW. AIS-based scenario simulation for the control and improvement of ship emissions in ports. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022;10(2):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10....
23.
Kim HS, Lee E, Lee EJ, Hyun JW, Gong IY, Kim K et al. A study on grid-cell-type maritime traffic distribution analysis based on AIS data for establishing a coastal maritime transportation network. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023;11(2):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11....
24.
Kniaziewicz T. Using information from AIS system in the modelling of emission of toxic compounds in exhaust gas from marine Diesel engines. Maritime Transport. Technical, Innovation and Research. Barcelona 2012.
25.
Kniaziewicz T, Zacharewicz M. Evaluation of adequacy of a model of a marine diesel engine based upon empirical research. Combustion Engines. 2020;181(2):40-45. https://doi.org/10.19206/CE-20....
26.
Kramel D, Muri H, Kim Y, Lonka R, Nielsen JB. Ringvold AL. Global shipping emissions from a well-to-wake perspective: the MariTEAM Model. Environ Sci Technol. 2021;55(22):15040-15050. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.es....
27.
Maragkogianni A, Papaefthimiou S, Zopounidis C. Mitigating Shipping Emissions in European ports: social and environmental benefits. Springer Cham. 2016. http://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-3....
28.
Matthias V, Bewersdorff I, Aulinger A, Quante M. The contribution of ship emissions to air pollution in the North Sea regions. Environ Pollut. 2010;158:2241-2250. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpo....
29.
Merico E, Donateo A, Gambaro A, Cesari D, Gregoris E, Barbaro E et. al. Influence of in-port ships emissions to gaseous atmospheric pollutants and to particulate matter of different sizes in a Mediterranean harbour in Italy. Atmos Environ. 2016;139:1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmo....
30.
Merkisz J, Piaseczny L, Kniaziewicz T. Zagadnienia emisji spalin silników okrętowych (in Polish). Wydawnictwo Politechniki Poznańskiej. Poznań 2016.
31.
Moreno-Gutiérrez J, Durán-Grados V. Calculating ships’ real emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases: towards zero uncertainties. Sci Total Environ. 2021;750:141471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scit....
32.
Ntziachristos L, Gkatzoflias D, Kouridis C, Samaras Z, COPERT: A European Road Transport Emission Inventory Model. In: Athanasiadis IN, Rizzoli AE, Mitkas PA, Gómez JM (eds). Information Technologies in Environmental Engineering. Environmental Science and Engineering. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg 2009. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-....
33.
Nunes RAO, Alvim-Ferraz MCM, Martins FG, Sousa SIV. The activity-based methodology to assess ship emissions – a review. Environ Pollut. 2017;231(1):87-103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envp....
34.
Ribeiro da Silva JN, Santos TA, Teixeira AP. Methodology for Predicting Maritime Traffic Ship Emissions Using Automatic Identification System Data. J Mar Sci Eng. 2024;12:320. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12....
35.
Richter A, Eyring V, Burrows JP, Bovensmann H, Lauer A, Sierk B et al. Satellite measurements of NO2 from international shipping emissions. Geophys Res Lett. 2004;31:1-4. http://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL0....
36.
Riveiro M, Pallotta G, Vespe M. Maritime anomaly detection: a review. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Data Min Knowl Discov. 2018;8:e1266. https://doi.org/10.1002/widm.1....
37.
Rong H, Teixeira AP, Guedes SC. Data mining approach to shipping route characterization and anomaly detection based on AIS data. Ocean Eng. 2020;198:106936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocea....
38.
Rong H, Teixeira AP, Guedes SC. Maritime traffic probabilistic prediction based on ship motion pattern extraction. Reliab Eng Syst Safe. 2022:217:108061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress....
39.
Rong H, Teixeira AP, Guedes SC. Spatial correlation analysis of near ship collision hotspots with local maritime traffic characteristics. Reliab Eng Syst Safe. 2021;209:107463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress....
40.
Saraçoglu H, Deniz C, Kiliç A. An investigation on the effects of ship sourced emissions in Izmir Port, Turkey. Sci World J. 2013;3:218324. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/2....
41.
Silveira PAM, Teixeira AP, Soares CG. Use of AIS data to characterise marine traffic patterns and ship collision risk off the coast of Portugal. J Navigation. 2013;66(6):879-898. https://doi.org/10.1017/S03734....
42.
Song S. Ship emissions inventory, social cost and eco-efficiency in Shanghai Yangshan port. Atmos Environ. 2014;82:288-297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmo....
43.
Song SK, Shon ZH. Current and future emission estimates of exhaust gases and particles from shipping at the largest port in Korea. Environ Sci Pollut R. 2014;21:6612-6622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356....
44.
Svanberg M, Santén V, Hörteborn A, Holm H, Finnsgård C. AIS in maritime research. Mar Policy. 2019;106:103520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marp....
45.
Tu E, Zhang G, Rachmawati L, Rajabally E, Huang GB, Exploiting AIS data for intelligent maritime navigation: a comprehensive survey from data to methodology. IEEE T Intell Transp. 2018;19(5):1559-1582. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2....
46.
Tzannatos E. Ship emissions and their externalities for the port of Piraeus – Greece. Atmos Environ. 2010;44(3):400-407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmo....
47.
Vinken GCM, Boersma KF, Maasakkers JD, Adon M, Martin RV. Worldwide biogenic soil NOx;emissions inferred from OMI NO2 observations. Atmos Chem Phys. 2014;14(18):10363-10381. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14....
48.
World Maritime News. COP21: Paris Remains Silent on Shipping and Aviation. 2016. http://worldmaritimenews.com/a....
49.
Wu G, Umar JA, Li T, Zhou X, Chen C, Li J, et al. Recent research progress on black carbon emissions from marine diesel engines. Atmosphere. 2024;15:22. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos1....
CITATIONS (1):
1.
Assessment of exhaust gas concentration uniformity in a marine engine duct based on dual-point sampling and CFD modelling
Magdalena Zimakowska-Laskowska, Artur Bogdanowicz, Tomasz Kniaziewicz
Combustion Engines
Magdalena Zimakowska-Laskowska, Artur Bogdanowicz, Tomasz Kniaziewicz
Combustion Engines
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.