Current issue
Online first
Archive
About the Journal
Aims and scope
Publisher and Editorial
Advertising policy
For Authors
Paper review procedures
Procedures protecting authentic authorship of papers
Paper preparation manual
Plagiarism check
Publication ethics
Reviewers
APC
Editorial and Scientific Board
Contact
Reviewers
Investigation of the influence of the propeller blade profile and angle of attack on the performance parameters of an aircraft piston engine
1
Faculty of Engineering, University of Technology and Economics H. Chodkowska in Warsaw, Poland
2
Faculty of Mechatronics, Armament and Aerospace, Military University of Technology, Poland
Submission date: 2025-04-03
Final revision date: 2025-07-13
Acceptance date: 2025-07-29
Online publication date: 2025-09-22
Publication date: 2026-01-14
Corresponding author
Piotr Wróblewski
Faculty of Engineering, University of Technology and Economics H. Chodkowska in Warsaw, Poland
Faculty of Engineering, University of Technology and Economics H. Chodkowska in Warsaw, Poland
Combustion Engines 2026,204(1), 119-131
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
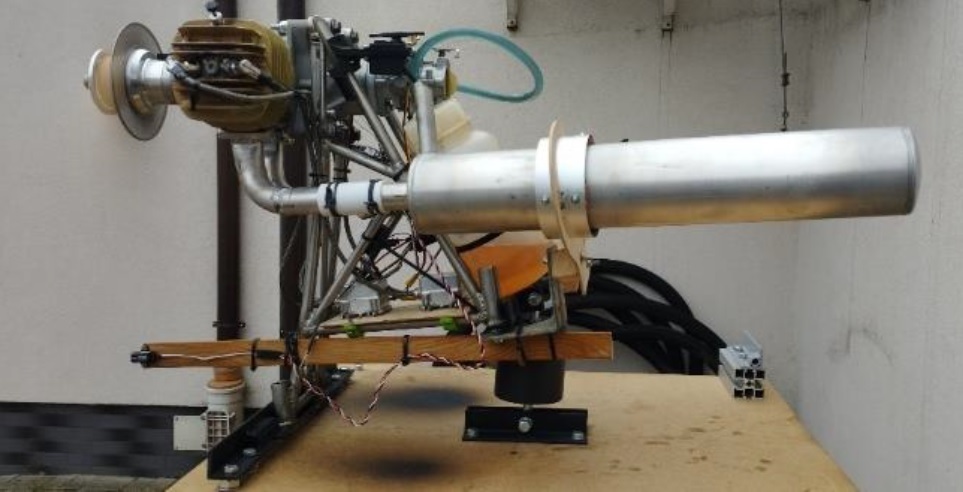
This article presents the results of experimental research concerning the influence of propeller blade profile and angle of attack on the performance parameters of the 3W 275 XI B2 CS aircraft piston engine. A specialised test stand was utilised, enabling real-time measurement of thrust, cylinder head temperature, and crankshaft rotational speed. The research was conducted with various propeller configurations (2- and 3-bladed) and at differing rotational speeds, which allowed for an assessment of the impact of propeller geometry on engine operational efficiency. The findings demonstrated that appropriate selection of the angle of attack, blade profile, and number of blades significantly affects the achieved parameters – particularly thrust and temperature distribution, which is of critical importance for the safety and durability of the powertrain components. The developed test stand facilitates further research into propeller selection for light aircraft piston combustion engines.
A novel aspect of this work is the utilisation of a new type of test stand that permits the determination of changes in thrust values obtained during tests across wide ranges of engine crankshaft rotational speeds. The selection of propellers, considering the number of blades and their profile, is very difficult to predict and should always be undertaken individually for each engine following testing. Such a tailored blade profile and number of propeller blades allow for high engine operational flexibility and good propeller thrust depending on the crankshaft's rotational speed.
REFERENCES (18)
1.
Balicki W. Potrzeby i sposoby diagnozowania lotniczych silników turbinowych (in Polish). Prace Instytutu Lotnictwa. 2009;4(199):109-116. https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/bazte....
2.
Błachnio J, Chalimoniuk M, Nidzgorska A. Selected appli-cations of composites in the military. J Konbin. 2023;53(4):191-210. https://doi.org/10.5604/01.300....
3.
Bonisławski A, Juchniewicz M, Piotrowski R. Projekt tech-niczny i budowa platformy latającej typu quadrocopter (in Polish). Pomiary Automatyka Robotyka. 2014;91-97.
4.
Dunna MH, Tinetti AF, Nark DM. Open rotor noise predic-tion using the time-domain formulations of Farassat. Aeroa-coustics. 2015;14(1-2);51-86.
5.
El-Sayed AF. Piston engines and propellers. El-Sayed AF, (ed.). Fundamentals of aircraft and rocket propulsion. Springer. London 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-....
6.
Federal Aviation Administration. Helicopter flying handbook. Chapter 4. Washington (DC): U.S. Department of Transportation; 2023. Available from: https://www.faa.gov/sites/faa.....
8.
Gosiewski Z, Ołdziej D, Słowik M. Identyfikacja modelu dynamicznego napędu dla śmigłowca czterowirnikowego (in Polish). Prace Instytutu Lotnictwa. 2009;7(202):36-50. https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/bazte....
9.
Kachel S, Okoń T, Frant M, Majcher M. Project for a recon-naissance unmanned aerial vehicle. J Konbin. 2022;52(3):187-200. https://doi.org/10.2478/jok-20....
10.
Kuźniar M. Wielokryterialna ocena doboru napędów lot-niczych nowej generacji z wykorzystaniem metod ener-getycznych [doctoral dissertation]. Rzeszów University of Technology. Rzeszow 2020.
11.
Miloudi M, Medles K, Tilmatine A, Brahami M, Dascalescu L. Modeling and optimization of a propeller-type tribocharger for granular materials. J Electrostat. 2011;69(6).
12.
Pawełczyk M, Bibik P. Wykorzystanie nowoczesnych narzędzi inżynierskich w projektowaniu bezzałogowego wiropłata czterowirnikowego (in Polish). Prace Instytutu Lotnictwa. 2013;3-4(230-231):103-110.
13.
Piłat M, Kaznowska A. Wielopłatowe, bezprzegubowe śmigło ogonowe do śmigłowca klasy lekkiej (in Polish). Prace Instytutu Lotnictwa. 2009;201:111-120.
14.
Roman K. Śmigłowcowe eksperymentalne – latające labora-toria na bazie śmigłowca IS-2 (in Polish). Prace Instytutu Lotnictwa. 2008;3-4:194-195.
15.
Sabak R. Zespoły napędowe bezzałogowych statków powietrznych (in Polish). Prace Instytutu Lotnictwa. 2011;213:185-188.
16.
Tiruvenkadam N, Shankar SG, Kumar PM, Gowtham S. Investigation of structural and thermal analysis of drone propeller materials. J Phys Conf Ser. 2024;2925(1):012002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6....
17.
Wróblewski P, Bratkowski P, Borcuch D, Kiszkowiak Ł. Prototype test stand for an aircraft piston engine for testing propeller profiles and advanced materials. Combustion En-gines. 2025;201(2):165-175. https://doi.org/10.19206/CE-20....
18.
Żmudziński Z. Kompozyty i inne materiały stosowane w konstrukcjach lotniczych (in Polish). Sprawozdanie ITWL 5134/50. Instytut Techniczny Wojsk Lotniczych. Warsaw 2009.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.