Current issue
Online first
Archive
About the Journal
Aims and scope
Publisher and Editorial
Advertising policy
For Authors
Paper review procedures
Procedures protecting authentic authorship of papers
Paper preparation manual
Plagiarism check
Publication ethics
Reviewers
APC
Editorial and Scientific Board
Contact
Reviewers
Correlation relationships of processes in the combustion engine in the RDE test
1
Automotive Development Institute in Bielsko-Biała, BOSMAL, Poland
2
Warsaw, Institute of Environmental Protection – National Research Institute, Poland
3
Faculty of Civil and Transport Engineering, Institute of IC Engines and Powertrains;
Poznan University of Technology, Poland
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2024-07-22
Final revision date: 2024-08-26
Acceptance date: 2024-09-02
Online publication date: 2024-10-01
Publication date: 2024-11-13
Combustion Engines 2024,199(4), 112-125
KEYWORDS
correlationfuel consumptionpollutant emissionReal Driving Emissions test (RDE)engine operating states
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
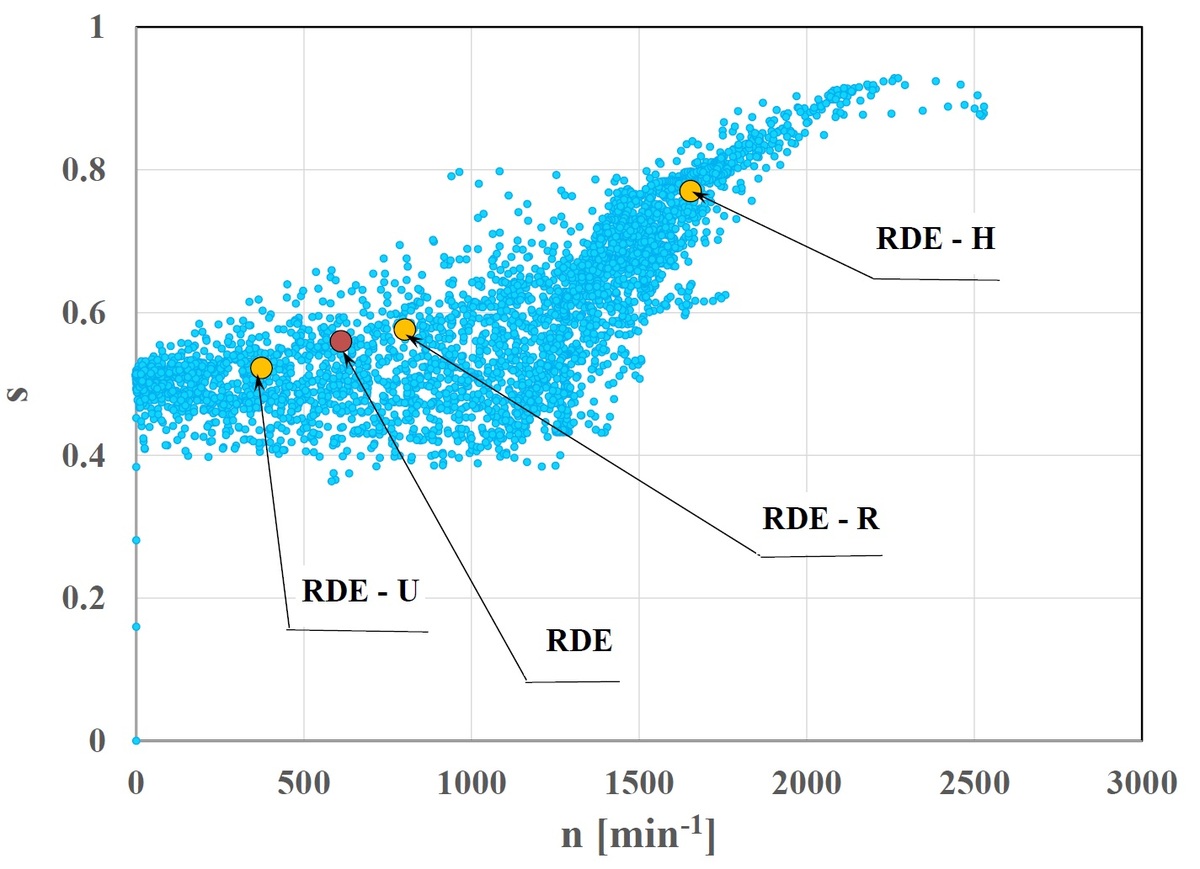
The article presents considerations on the processes taking place in the combustion engine in the in real driving operating conditions of a vehicle performing the RDE (Real Driving Emissions) test. The tests were carried out using a passenger car with a spark-ignition engine. The processes considered in the article were related to the engine operating states, exhaust emissions and fuel consumption, and the vehicle speed, which determines the engine operating conditions. The RDE test were carried out using PEMS (Portable Emissions Measurement System) equipment, and the following variables were recorded: vehicle speed, control, rotational speed, relative torque and relative engine power, emission pollutant intensity of: carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxides and carbon dioxide, the intensity of particle number and the fuel consumption intensity. The recorded signals were digitally processed, and the statistical properties of the variables and the mutual relation between the engine operating states were examined. The properties of the measured variables were investigated in the entire RDE test and in its constituent phases: the first, corresponding to vehicle movement in cities, the second – outside cities, and the third – on highways and expressways. The pollutant specific distance emission and the particle number specific distance as well as the specific distance fuel consumption were determined in relation to the average vehicle speed, and based on these results, the exhaust emissions and fuel consumption characteristics were created. Correlational studies of the considered variables were also performed. Pearson's linear correlation coefficients for the measured variables combinations were determined.
REFERENCES (39)
1.
André M, Joumard R, Vidon R, Tassel P, Perrte P. Real-world European driving cycles, for measuring pollutant emissions from high- and low-powered cars. Atmos Environ. 2006;40(31):5944-5953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmo....
2.
André M. The ARTEMIS European driving cycles for measuring car pollutant emissions. Sci Total Environ. 2004;334-335:73-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scit....
3.
Andrych-Zalewska M, Chłopek Z, Merkisz J, Pielecha J. Analysis of the operation states of internal combustion engine in the Real Driving Emissions test. Archives of Transport. 2022;61(1): 71-88. https://doi.org/10.5604/01.300....
4.
Andrych-Zalewska M, Chłopek Z, Merkisz J, Pielecha J. Exhaust emission from a vehicle engine operating in dynamic states and conditions corresponding to real driving. Combustion Engines. 2019;178(3):99-105. https://doi.org/10.19206/CE-20....
5.
Andrych-Zalewska M, Chłopek Z, Merkisz J, Pielecha J. Investigations of exhaust emissions from a combustion engine under simulated actual operating conditions in real driving emissions test. Energies. 2021;14(4):935. https://doi.org/10.3390/en1404....
6.
Andrych-Zalewska M, Chłopek Z, Merkisz J, Pielecha J. Research on exhaust emissions in dynamic operating states of a combustion engine in a Real Driving Emissions test. Energies. 2021, 14(18), 5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/en1418....
8.
Bebkiewicz K, Chłopek Z, Sar H, Szczepański K, Zimakowska-Laskowska M. Assessment of impact of vehicle traffic conditions: urban, rural and highway, on the results of pollutant emissions inventory. Archives of Transport. 2021;60(4);57-69. https://doi.org/10.5604/01.300....
9.
Bendat JS, Piersol AG. Random data: analysis and measurement procedures. John Wiley & Sons, 2010. Book Series: Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics. https://doi.org/10.1002/978111....
10.
BUWAL (Bundesamt für Umwelt, Wald und Landschaft), INFRAS AG (Infrastruktur-, Umwelt- und Wirtschaftsberatung). Luftschadstoffemissionen des Strassenverkehrs 1950–2010, BUWAL-Bericht 1995; 255.
11.
Chłopek Z, Biedrzycki J, Lasocki J, Wójcik P, Samson-Bręk I. Modelling of motor vehicle operation for the evaluation of pollutant emission and fuel consumption. Combustion Engines. 2017;171(4):156-63. https://doi.org/10.19206/CE-20....
12.
Chłopek Z, Biedrzycki J, Lasocki J, Wójcik P. Assessment of the impact of dynamic states of an internal combustion engine on its operational properties. Eksploat Niezawodn. 2015;17(1):35-41.
13.
Chłopek Z, Biedrzycki J, Lasocki J, Wójcik P. Correlational investigation of air pollutant emissions and fuel consumption of motor vehicle in various dynamic conditions. Global NEST J. 2020;22(2):275-279. https://doi.org/10.30955/gnj.0....
14.
Chłopek Z, Lasocki J. Correlation investigations into pollutant emission and the operational states of compression-ignition engines in dynamic tests. Combustion Engines. 2017;169(2):87-92. https://doi.org/10.19206/CE-20....
15.
Chłopek Z. A correlation analysis of the pollutant emission from a self ignition engine. Silniki Spalinowe – Combustion Engines. 2010;140(1):25-31. https://doi.org/10.19206/CE-11....
16.
Chłopek Z. Analysis of the correlation between pollutant emissions and operation states of a compression ignition engine. The Archives of Automotive Engineering – Archiwum Motoryzacji. 2015;68(2):3-19.
17.
Chłopek Z. Some remarks on engine testing in dynamic states. Combustion Engines. 2010;143(4):60-72. https://doi.org/10.19206/CE-11....
19.
Croux C, Dehon C. Influence functions of the Spearman and Kendall correlation measures. Stat Method Appl. 2010;19:497-515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10260....
22.
Giechaskiel B, Vlachos T, Riccobono F, Forni F, Colombo R, Montigny F et al. Implementation of Portable Emissions Measurement Systems (PEMS) for the Real-Driving Emissions (RDE) regulation in Europe. JOVE-J Vis Exp. 2016;118:54753. https://doi.org/10.3791/54753.
23.
INFRAS AG. Handbook emission factors for road transport 3.2. Quick reference. Version 3.2. Bern, 2014.
25.
Lane D. Introduction to statistics – Open Textbook Library, 2003. https://open.umn.edu/opentextb....
26.
Luján J M, Piqueras P, de la Morena J, Redondo F. Experimental characterization of real driving cycles in a light-duty diesel engine under different dynamic conditions. Appl Sci. 2022;12(5):2472. https://doi.org/10.3390/app120....
27.
Metsämuuronen J. Dimension-corrected Somers' d for the item analysis settings. Int J Educ Method. 2020;6(2):297-317. https://doi.org/10.12973/ijem.....
28.
Papoulis A, Pillai SU. Probability, random variables, and stochastic processes. Tata McGraw-Hill, 2002;852.
30.
Pearson K. Determination of the coefficient of correlation. Science. 1909;30(757):23-25. https://doi.org/10.1126/scienc....
31.
Pearson K. Note on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. P R Soc London. 1895;58:240-242. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspl.1....
33.
Pielecha J, Skobiej K, Kurtyka K. Exhaust emissions and energy consumption analysis of conventional, hybrid, and electric vehicles in real driving cycles. Energies. 2020;13(23):6423. https://doi.org/10.3390/en1323....
34.
Savitzky A, Golay MJE. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal Chem. 1964;36(8):1627-1639. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac6021....
35.
Sedgwick PM. Spearman's rank correlation coefficient. BMJ Brit Med J. 2014;3497327. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7....
36.
Semtech-DS On Board Vehicle Emissions Analyzer (2010). User Manual. Document: 9510086, Revision: 2.01.
38.
Wang Z, Wu P, Yu N, Zhang Y, Wang Z. Analysis of the influence of RDE test data processing methods on the emission results of China 6 light duty vehicles. E3S Web Conf. 2021;268:01022. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3scon....
39.
Worldwide emission standards (2021/2022). Passenger cars and light duty vehicles. Delphi. Innovation for the real world.
CITATIONS (2):
1.
Research on fuel and electric energy consumption in passenger cars in a mixed cycle, using the example of local road traffic in Opole
Maciej Sproch, Jarosław Mamala, Andrzej Augustynowicz, Mariusz Graba
Combustion Engines
Maciej Sproch, Jarosław Mamala, Andrzej Augustynowicz, Mariusz Graba
Combustion Engines
2.
Comparative analysis of exhaust emissions from a compression-ignition engine fueled with mixtures of rapeseed oil with n-hexane and diesel fuel during selected phases of the WLTP test
Rafał Longwic, Michał Kuszneruk, Mateusz Maciej Klepka
Combustion Engines
Rafał Longwic, Michał Kuszneruk, Mateusz Maciej Klepka
Combustion Engines
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.